Shapes of orbitals depends upon the quantum numbers. So for four types of orbitals have been introduced depending upon the values of azimuthal quantum number. These orbitals are s, p, d, and f, having azimuthal quantum number values as l= 0, 1, 2, 3, respectively. Let us discuss the shapes of these orbitals.
Shape of Orbitals for s-subshell
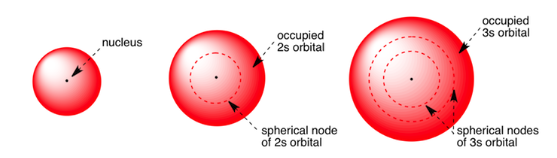
The s-orbital has a spherical shape and is usually represented by a circle, which represents a cut of the sphere. With the increase of the value of the principal quantum number (n), the size of s-orbital increases. 2s-orbital is larger than 1s-orbital. 2s orbital is further away from the nucleus. The probability of finding the electron is zero between two orbitals. This place is called the nodal plane or nodal surface.
Shapes of Orbitals for p subshell
There are three values of the magnetic quantum number which give arise a set for shapes of orbitals with respect to p sub-shell. So p subshell has three orientations in space, i.e., along x, y, and z-axis. All three p orbitals, namely Px, Py, and Pz, have a dumb-bell shape.
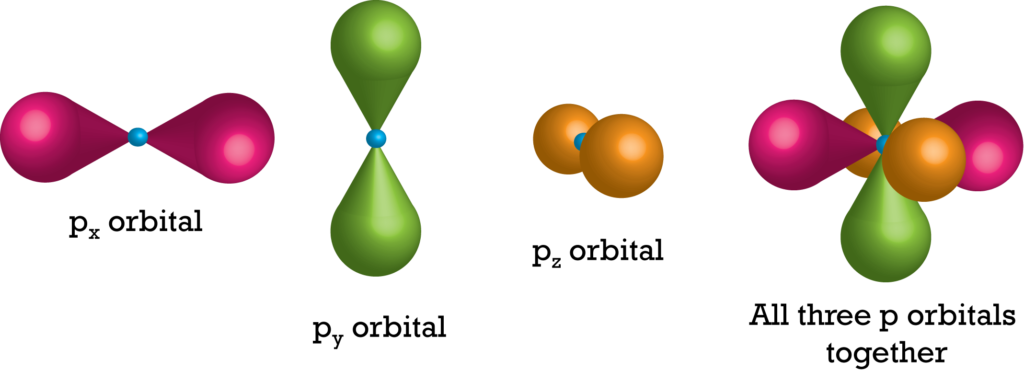
Therefore, p-orbitals have directional character, which determines the geometry of molecules. All the p-orbitals of all the energy levels have a similar shape. However, with the increase of the principal quantum number of the shell, their size is increased.
Shapes of d-Orbitals
For the d sub-shell, there are five values of the magnetic quantum number. So there is five space orientation, and it can be arranged in space in five different ways along x, y, and z-axes.
They are designated dxy, dyz, dxz, dx2-y2, dz2.
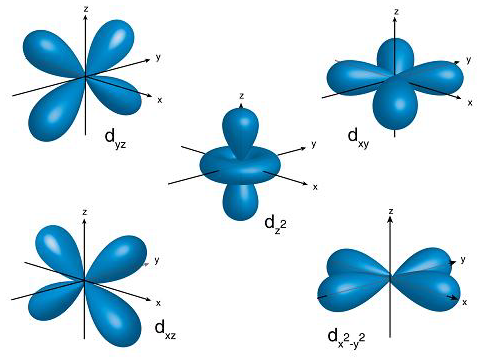
They are not identical in shape. Four d-orbital out of these five contain four lobes, while the fifth orbital dz2 consists of only two lobs.
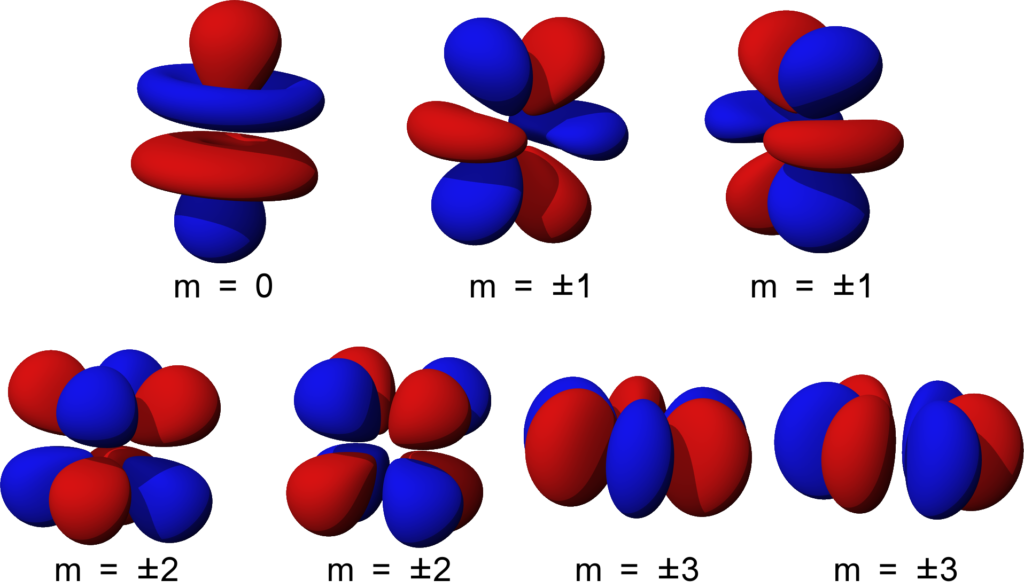
Shapes of Orbitals for f subshell
In the absence of a magnetic field, all five d-orbitals are degenerate. The orbital is much more complicated, but follows the very same rules based on proton orientation as the p and d orbitals. When completely fill it is like the d orbital, but cut in half (eight lobes rather than four). It is founded upon the points at the nucleus rotation.




4 Comments
As a new comer I am satisfied with this website cause it contains good content…
Thanks for visiting and finding worth it to give time on our website. Keep visiting and sharing with your friends.
Should post the books ASAP. IAM really excited…
Daily there will be one eBook.