Electrolysis Chemistry
Electrolysis Chemistry or Electrochemistry is the study of the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy in electrolytic cells as well as the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy in Galvanic or Voltaic cell.
Electrolysis Chemistry or Electrochemistry is extensive Branch of chemistry. So, it cannot be summed in a single article. However, for your convenience, the following are some important terms & definitions we use in electrolysis chemistry or Electrochemistry.
Electrolysis:
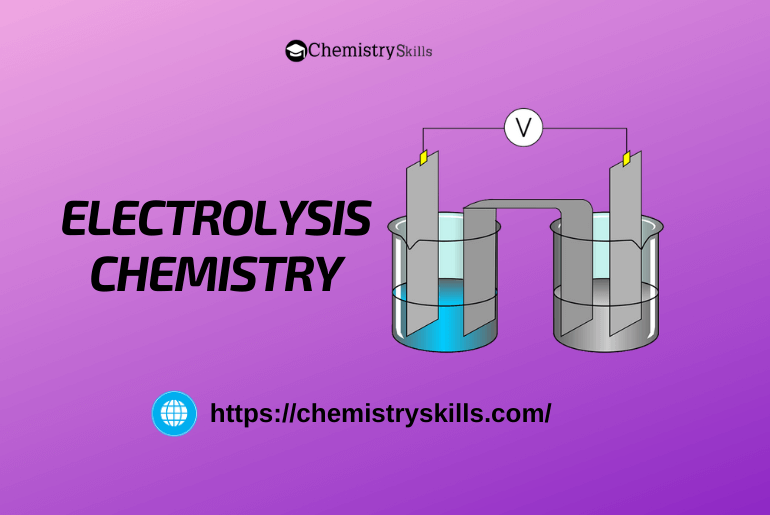
The process in which non-spontaneous redox reaction occurs at the electrodes by the passage of electric current is called electrolysis.
The process in which non-spontaneous redox reaction takes place at the electrodes by the passage of electric current is called electrolysis. Note:
For electrolysis, an electric current is passed through the aqueous or molten state of electrolyte taken in the electrolytic cell.
Explanation:
When electricity is passed through an electrolyte anion, begin to move towards Anode (i.e., positively charged electrode). In contrast, cations begin to move towards cathode or (i.e., os negatively = Positive ion charged electrode). Oxidation 0 = Negative ion takes place at the anode, which removes electrons from the anions, whereas reduction takes place at the cathode, which provides electrons to the cations.
Note:
For electrolysis, an electric current is passed through the aqueous or molten state of electrolyte taken in the electrolytic cell.
Oxidation: Such a chemical reaction during which,
• Electron is removed
• or Hydrogen is removed
• or Oxygen is added
• or Oxidation number increases
Reduction: Such a chemical reaction during which,
• Electron is added
• Or Hydrogen is added
• Oxygen is removed
• Oxidation number decreases
Oxidizing Agent
Such a chemical agent which oxidizes other substance but reduces itself is called an oxidizing agent.
Example: Potassium permanganate (KMnO4)
Reducing Agent
Such a chemical agent which reduces other substances but oxidizes itself is called
reducing agent.
Example: Nascent hydrogen [H]
Valency
- Definition: The apparent charge (positive, negative or the combining capacity of an element with zero) which an atom would have in a molecule other elements is called Valency.
- Representation: it can be in whole number and fractional number. It is always in the whole number.
- Value: It can be zero.
It cannot be zero except for noble gases.
Metallic Conduction:
The movement of electrons throughout the metallic lattice by the application of electricity is called metallic conduction.
Electrolytic Conduction:
The movement of ionic charges through the liquid, brought about by the application of electricity is called electrolytic conduction.
Explanation:
In electrolytic conduction, an electric current is passed through ions. During electrolytic conduction chemical reaction takes place. The anions of the electrolyte move towards the anode, where they are oxidized, whereas the cations of the electrolyte move towards cathode, where they are reduced. The electrons, which are given by the anions to the anode during their oxidation, are pumped out by the source of electric potential and transferred to the cathode, where they are required for reduction of cations.
Electrochemical cells
The cells in which interconversions of electrical & chemical energies takes place are called Electrochemical cells.
Electrolytic cells
The electrochemical cells in which a non-spontaneous redox reaction consumes the electrical energy and proceeds is called electrolytic cell. Example of electrolytic cells is Down’s cell, Nelson’s cell etc.
Galvanic Cell
The electrochemical cells in which a spontaneous redox reaction proceeds and produces electrical energy is called Voltaic or Galvanic cell. Examples of Galvanic cells are Daniel’s cell, Ni-Cd cell, fuel cell etc.
Electromotive Force (emf) of Voltaic Cell
The force with which the electrons are pushed to flow through the wire from the negative electrode to the positive electrode of a Galvanic cell is called Electromotive force, i.e., emf.
Electrode Potential
The potential difference set up between the metal and its ion’s surrounding is called single electrode potential.
Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)
A standard hydrogen electrode consists of a platinum foil coated with
Lead to potentiometer a layer of finely divided platinum wire. – It is encased with a glass sleeve with
Supply of hydrogen gas passing through it at 1 atm pressure.
It is then immersed in a 1 M HCl solution. The reduction potential of SHE is arbitrarily decided as zero.
Escaping bubbles of SHE acts as the anode.
The Electrochemical Series
The list of elements arranged in the order of their standard electrode potentials on the hydrogen scale is called electrochemical series.
Lead Accumulator (Lead Storage Battery)
The lead accumulator is also known as a lead storage battery. It is used as a car battery. It delivers either 6 or 12 V, depending on the number of cells used in its construction.
Alkaline battery (non-rechargeable)
This is a type of dry cell. It uses zinc and manganese dioxide as reactants. In this cell, zinc acts as the anode, whereas manganese dioxide acts as a cathode. The electrolyte consists of potassium hydroxide. The zinc anode used is slightly porous, which provides a larger effective area.
Silver oxide battery
This is a tiny battery, which is used in electronic wristwatches, auto exposure cameras and electronic calculators.
Fuel cell
A cell in which gaseous fuels are allowed to react in a carefully designed environment.
This cell consists of three compartments separated from each other by porous • electrodes made of carbon-containing platinum.