An analytical procedure in which an organic compound is burnt to determine the percentage of each element present in the compound is called combustion analysis.
In combustion analysis, weighed amount of an organic compound is burnt in the stream of oxygen in a closed tube known as combustion tube. At the end of this tube CuO is placed to ensure that combustion has been completed.
The hydrogen and carbon present in the compound convert into H2O vapour and carbon dioxide, respectively. A pre-weighed substance like Mg (ClO4)2 or CaCl2 absorbs the water vapours. Carbon dioxide is absorbed by a pre-weighed solution of potassium hydroxide.
The increase in the weights of these absorbers give the weight of CO2 and H2O vapours formed during combustion. These weights are used to calculate the percentage of each element by using the following formulas:
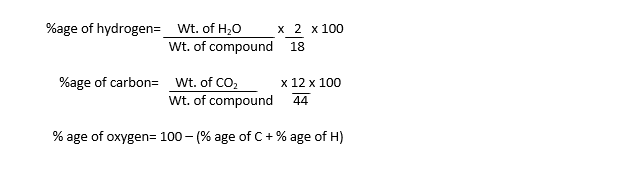
These percentages are used to determine empirical formula, which is further used to determine molecular formula.
Determination of empirical formula:
Following steps are carried out to determine the empirical formula:
i) % age of each element is divided by atomic mass of the element to get the
mole ratio.
ii) Mole ratios are divided by the smallest quotient to get the atomic ratio.
iii) If the resulting values are simple whole number well and good, otherwise multiply with a suitable figure to get so.
iv) Write down the empirical formula by writing the above-calculated ratios just after but below the symbol of each element.
Determination of molecular formula:
Following steps are carried out to determine the molecular formula of a compound:
i) Divide the molecular mass by the empirical formula mass to get the value ‘n’.
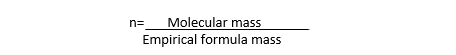
ii) Multiply the empirical formula by ‘n’ to get the molecular formula.
Molecular formula = n x empirical formula



