Spectrum
A visual display or dispersion of components of white light, when it is passed through a prism is called a spectrum.
Explanation:
When radiation of light is passed through a prism, the radiation undergoes refraction or bending. The extent of bending depends upon the wavelength of photons. Radiation of longer wavelength is bent to a smaller degree than the radiation of a shorter wavelength. Ordinary white light consists of radiation of all wavelengths, so after passing through the prism, white light is split up into radiations of different wavelengths.
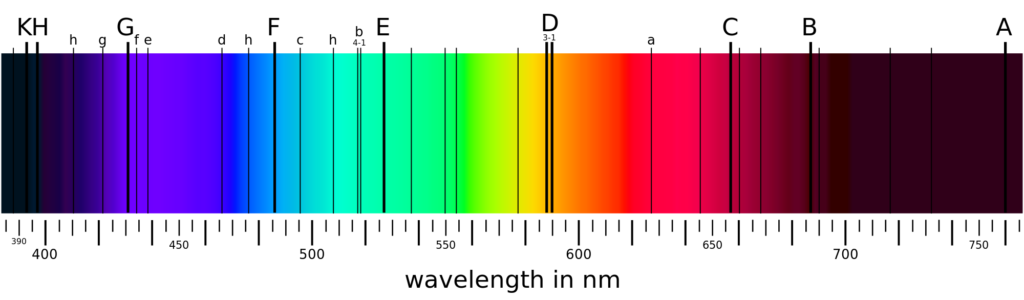
The Colours of the visible spectrum are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange-red, and they range from 400 nm to 750 nm (1 nm = 10-om). In addition to the visible region, there are seven other regions of the spectrum. Ultraviolet, X-rays, y-rays and cosmic rays are towards the lower wavelength end of the spectrum, and they possess the photons with greater energies. On the other side of the visible region, there lie infrared, microwave and radiofrequency regions.
Types of Spectrum
1. Continuous spectrum
2. Line spectrum
Continuous Spectrum In this type of spectrum, the boundary line between the Colours cannot be marked. The Colours diffuse into each other. One colour merges into another without any dark space; the best example of a continuous spectrum is rainbow. It is obtained from the light emitted by the sun or incandescent (electric light) solids. It is the characteristic of matter in bulk.
Atomic or Line Spectrum
When an element or its compound is volatilized on a flame and the light emitted is seen through a spectrometer, we see distinct lines separated by dark spaces. This type of spectrum is called a line spectrum or atomic spectrum. This is a characteristic of an atom. The number of lines and the distance between them depends upon the element volatilized. For example, the line spectrum of sodium contains two yellow coloured lines separated by a definite distance. Similarly, the spectrum of hydrogen consists of several lines of different Colours having different distances from each other. It has also been observed that the distance between the lines decreases with the decrease in wavelength and the spectrum becomes continuous after a specific value of wavelength.
Atomic spectrum can also be observed when elements in the gaseous state are heated at high temperature or subjected to an electric discharge.
Atomic Emission Spectrum
When solids are volatilized or elements in their gaseous states are heated to high temperature or subjected to an electrical discharge, radiation of specific wavelengths is emitted. The spectrum of this radiation contained bright lines against a dark background. This is called an emission spectrum.

Atomic Absorption Spectrum
When a beam of white light is passed through a gaseous sample of an element, the element absorbs specific wavelengths while the rest of wavelength pass through it. The spectrum of this radiation is called an atomic absorption spectrum. The wavelengths of the radiation that have been absorbed by the element appear as dark lines, and the background is bright.
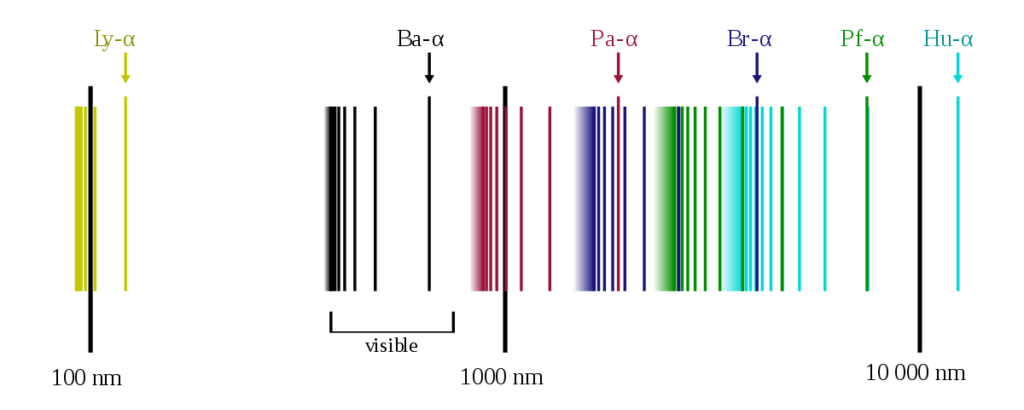
It is interesting to note that the positions or the wavelengths of lines appearing in both emission and absorption spectra are the same. In emission spectra, these lines appear bright because the corresponding wavelengths are being emitted by the element, whereas they appear dark in absorption spectra because the element is absorbing the wavelengths.