Definition:
The electrostatic force between a hydrogen atom bonded to a strongly electronegative atom and Hydrogen bond lone pair electrons of another Covalent bond strongly electronegative atom is called hydrogen bonding.
Strength:
Hydrogen bonds are not really chemical bonds in formal sense. These are weaker than covalent bond. However, hydrogen bonds are stronger than dipole-dipole interactions, which are stronger than London dispersion forces.
Explanation with examples:
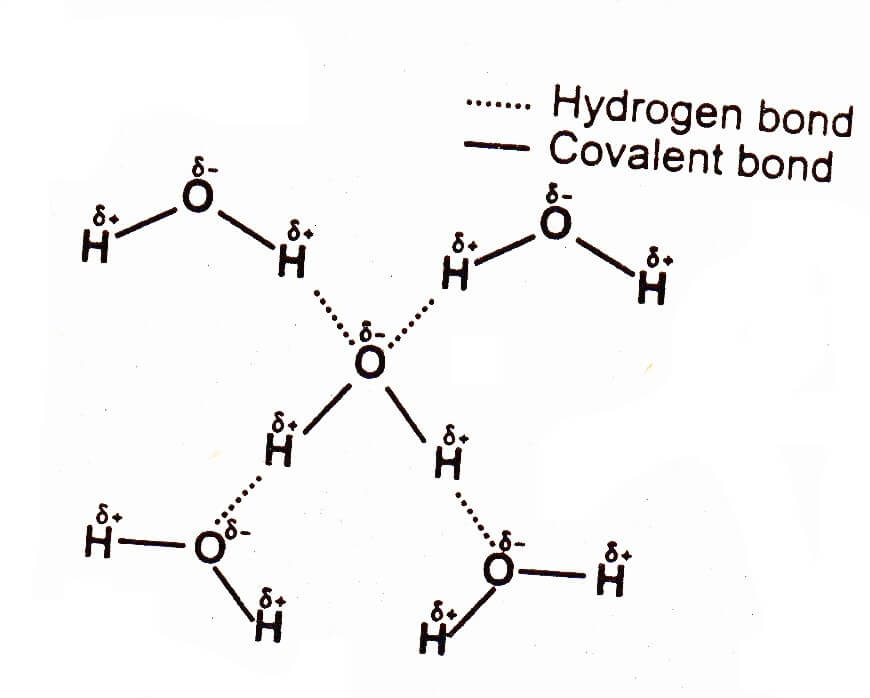
Hydrogen bonding in water
Hydrogen bonding occurs among polar covalent molecule containing H and one of the small, sized strongly electronegative elements such as N, O or F. Hydrogen bonding occurs in NH3, H2O, and HF etc. The boiling point and heat of vaporization of H2O are higher than those of H2S. This is because H2O molecules attract each other through hydrogen bonding whereas H2S molecules attract each other through dipole-dipole interactions, which is a weaker attractive force than hydrogen bonding.
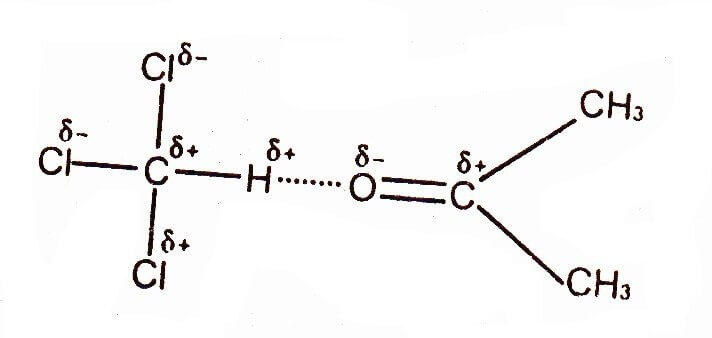
Hydrogen Bonding between Chloroform & Acetone
Hydrogen bonding does not limit to above-mentioned electronegative atom. The three chlorine atoms in chloroform are responsible for H-bonding with other molecules. These atoms deprive the carbon atom of its electrons and the partial positively charged hydrogen can form a strong hydrogen bond with Chloroform and Acetone.
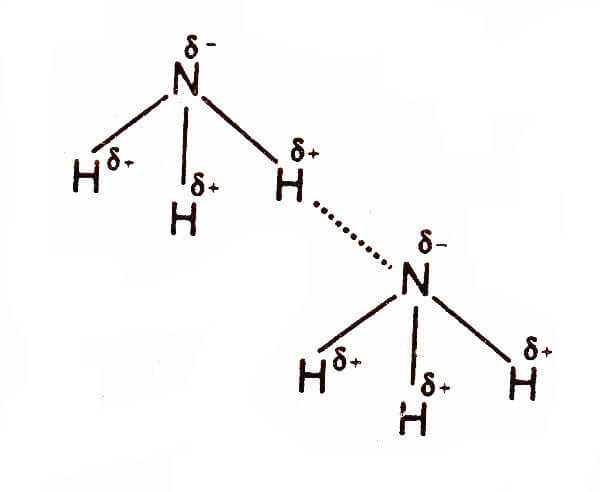
Hydrogen Bonding in Ammonia
Hydrogen Bonding in Hydrofluoric acid (HF is weaker acid than HCl & HBr)
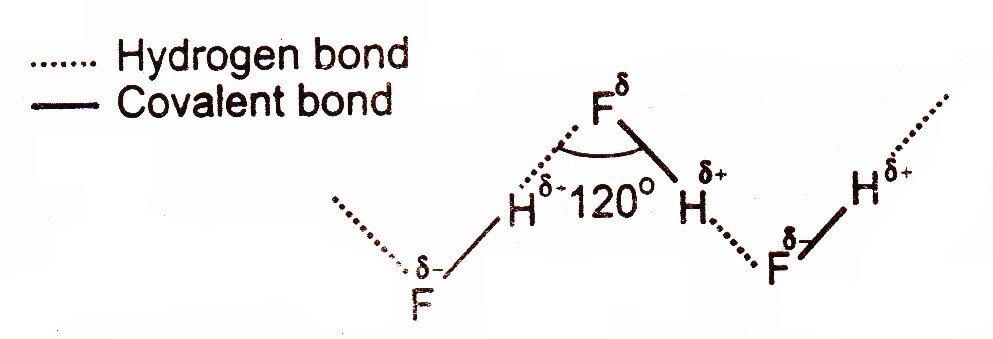
The exceptional, low acidic strength of HF molecule as compared to HCl, HBr, HI is due to this strong hydrogen bonding, because the partial positively charged hydrogen is entrapped between two highly electronegative atoms. So, hydrogen bonding is the electrostatic force of attraction between partial positive hydrogen atom and a highly electronegative atom like F, O and N belonging to another molecule. The stronger hydrogen bonding between H and F hardly allows hydrogen to become a proton as compared to HCl or HBr.
Importance of Hydrogen Bonding:
- Thermodynamic properties of covalent hydrides.
- Solubility of hydrogen-bonded molecules.
- Structure of ice.
- Cleansing action of soaps and detergents
- Hydrogen bonding in biological compounds and food materials.
- Hydrogen bonding in paints, dyes and textile materials.
Hydrogen bonding in DNA and RNA
Application of Hydrogen Bonding in DNA and RNA (Biological Compounds)
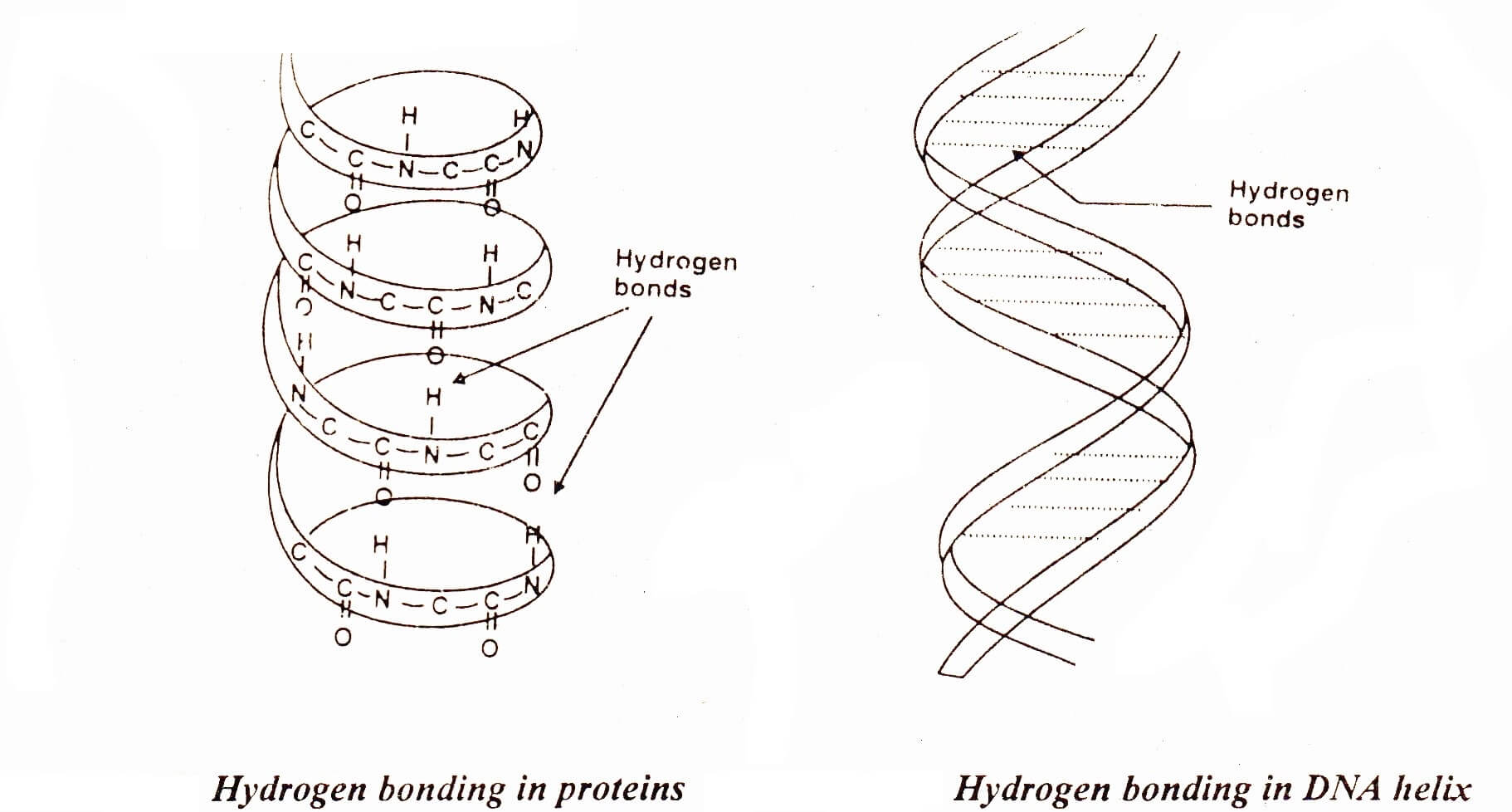
The molecules of living system contain hydrogen bonding. Proteins are the important part of living organisms. Hair, silk and muscles consist of long chains of amino acids. These long chains are coiled about one another into a spiral. This spiral is called a helix. Such a helix may either be right handed or left handed. In the case of right handed helix the groups like >NH and > C=O are vertically adjacent to one another and they are linked together by hydrogen bonds. These H-bonds link one spiral to the other. X-rays analysis has shown that on the average there are 27 amino acid units for each turn of the helix. .
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) has two spiral chains. These are coiled about each other on a common axis. In this way, they give a double helix. This is 18-20 Å in diameter. They are linked together by H-bonding between their sub-units.
Hydrogen Bonding in Paints and Dyes
In paints and dyes adhesive action is developed due to hydrogen bonding. Similar type of hydrogen bonding makes glue and honey sticky substances.
Hydrogen Bonding in Clothing & Food materials
We use cotton, silk or synthetic fibers for clotting. Hydrogen bonding is of vital importance in these thread making materials. This hydrogen bonding is responsible for their rigidity and the tensile strength.
Food materials like carbohydrates including glucose, fructose and sucrose all have -OH groups responsible for hydrogen bonding.
Structure of Ice
The electronic structure of water is tetrahedral. Two lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom occupy two corners of the tetrahedron. In the liquid state, water molecules are extensively associated with each other and these associations break and are reformed because the molecules of water are mobile. But associations go on breaking and forming because the molecules of the liquid are mobile.




2 Comments
an excellent and detail lec
Thanks for appreciation. Visit again for latest knowledge base articles.